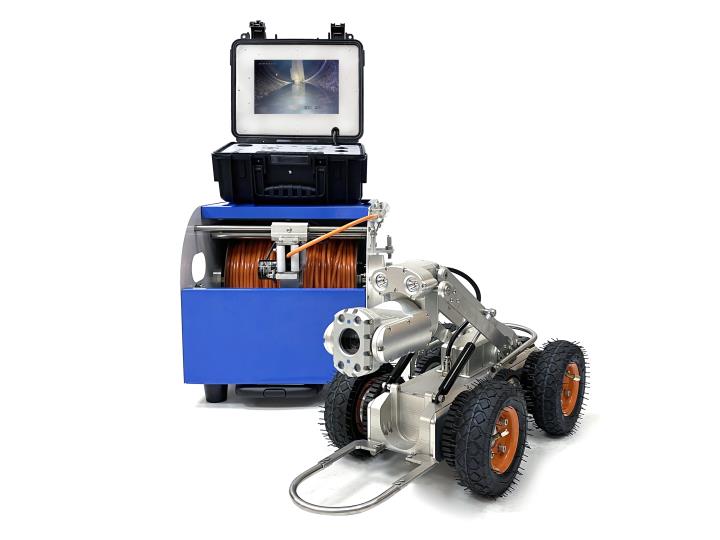
Sewer pipeline inspection robot systems development in furture.
These challenges involve multiple aspects such as technology, environment, operation, and cost. The following is a specific analysis of these challenges.
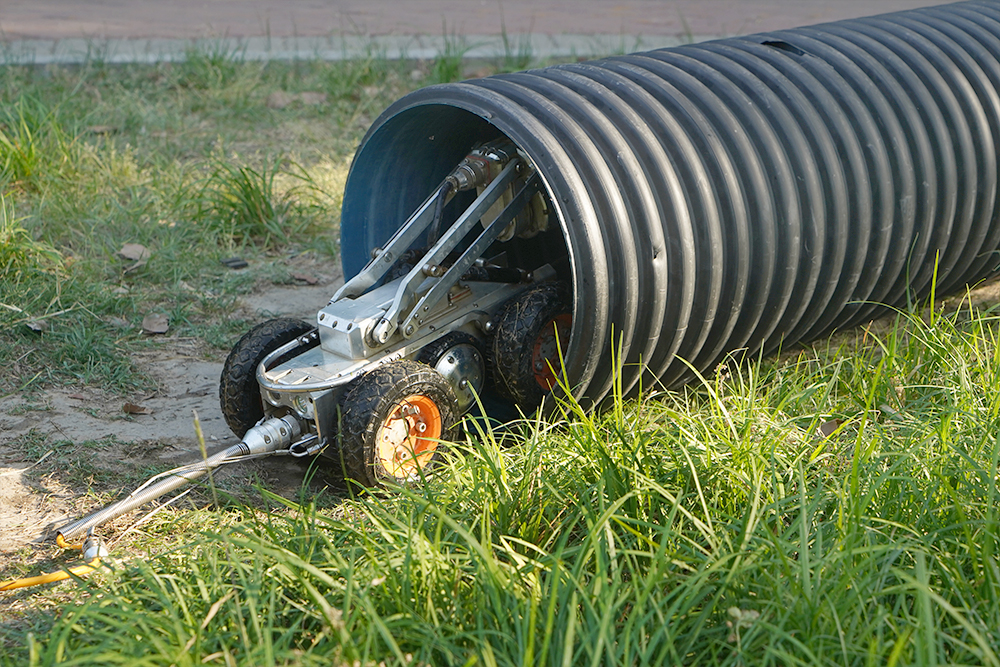

1. Technical challenges
Adaptability to complex environments:
The internal environment of pipelines is complex and changeable, including narrow bends, different diameters, and possible obstacles and dirt. This requires sewer pipe inspection robots camera to be able to flexibly cope with various complex environments.
High-precision sensors:
In order to accurately detect defects and abnormalities inside the pipeline, pipeline inspection robots need to be equipped with high-definition cameras, sonar, laser measurement, etc. However, the performance and accuracy of these sensors directly affect the accuracy of the detection results, so the technical challenges cannot be ignored.
Image processing and data analysis:
A large amount of image and video data will be generated during the operation of pipeline CCTV inspection crawler robots, which need to be processed and analyzed quickly and accurately. At present, although computer vision and machine learning technologies have been applied, how to automatically identify and classify defect types in complex environments is still a technical problem.
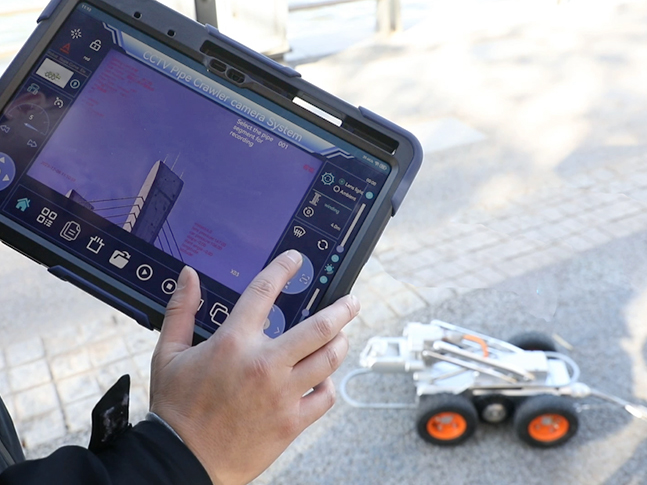

2. Environmental challenges
Harsh working environment:
The inside of the pipeline is usually in a humid, dark, and even toxic and harmful environment, which places high demands on the material selection, sealing performance, and waterproof level of drain pipe inspect robotic camera.
Unknown risk factors:
During the inspection process, the robot may encounter unknown obstacles, damage or leakage, which may pose a threat to the safety of the pipeline NDT inspection robot system.

3. Energy supply
Battery life:
Sewage Inspection robots work in pipelines for a long time, and the battery life may not meet the needs. Especially in complex pipe environments, sewer robots camera need to consume more power to overcome obstacles and inspection tasks.
4. Operational challenges
Remote control difficulty:
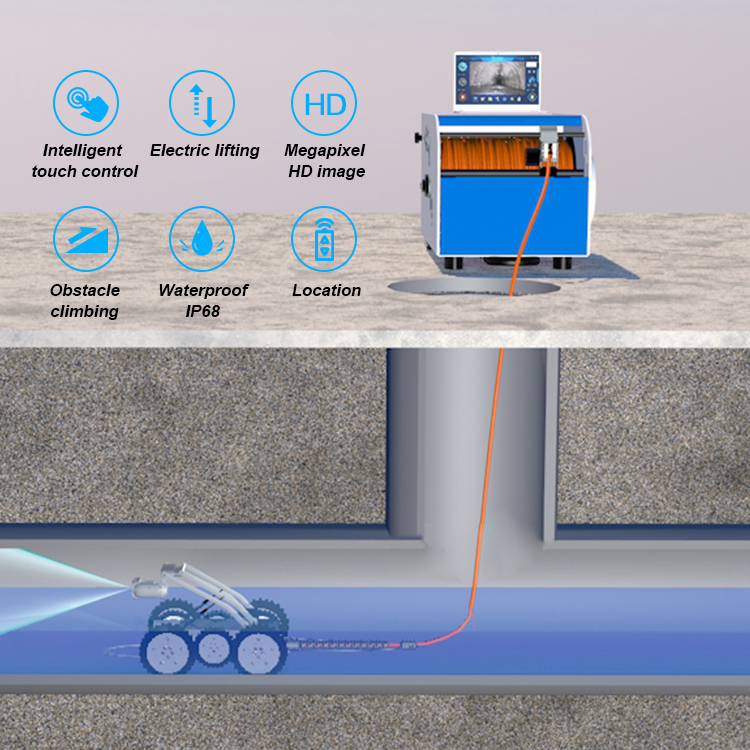
Due to the complex internal environment of the pipeline, it is difficult for operators to directly observe the working conditions of the CCTV pipe robot, so it is necessary to use a remote control system to control the pipeline inspection robot.
High operating skills requirements:
Operators need to have certain professional skills and experience to master the operation methods and troubleshooting skills of pipeline crawling robots. This puts higher requirements on the training and management of operators.
5. Cost challenges
Equipment cost:
High-precision sensors, image processing equipment, remote control systems, etc. are all important components of the pipe inspection robot system. The cost of these devices is relatively high, which increases the overall cost of the system.
Maintenance cost:
The robot system needs regular maintenance and care during long-term use to ensure its performance and stability. This will also bring certain maintenance costs.
6. Other challenges
Standards and specifications:
At present, there is no unified standard in the pipeline inspection robot industry. Products produced by different manufacturers may differ in performance, interface, data format, etc., which is not conducive to system integration and mutual applicability.
Market acceptance:
Although pipeline inspection robots have many advantages, market acceptance is still limited in some regions and fields due to the inertial thinking and cost considerations of traditional inspection methods.
At present, China's better manufacturers in the pipeline inspection camera system industry are: Zhengzhou Jiutai Technology; Schroders Industries Group; Wuhan Easy-sight etc.
In summary, pipeline inspection robot systems need to face many challenges in practical applications. In order to overcome these challenges, it is necessary to continuously strengthen technology research and development, improve equipment performance, optimize operating procedures, reduce costs, and promote the formulation and implementation of industry standards and specifications.






